4 October 2021
Asia-Pacific (ex-Japan) equities marginally fell year-to-date (as of 24 September) amid substantial dispersion among markets1. The recent resurgence of COVID-19 cases, coupled with rising inflation across the globe and volatility in China, has raised questions about the pace of the economic recovery and the trajectory of regional equity markets. In this investment note, our Asian Equities investment team outlines the key factors that will drive equities for the remainder of 2021. Although the divergence in regional performance is expected to continue, we believe the broad Asian equity universe offers attractive opportunities for active managers to find diversification and reasonably-valued companies.
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, both last year and into 2021, we foresaw a divergence in the performance of Asian equity markets. In 2020, those East Asian markets with superior virus containment measures and relatively higher inoculation rates led the region, while ASEAN countries lagged due to concentrated urban populations, limited access to vaccines, and less developed healthcare infrastructure.
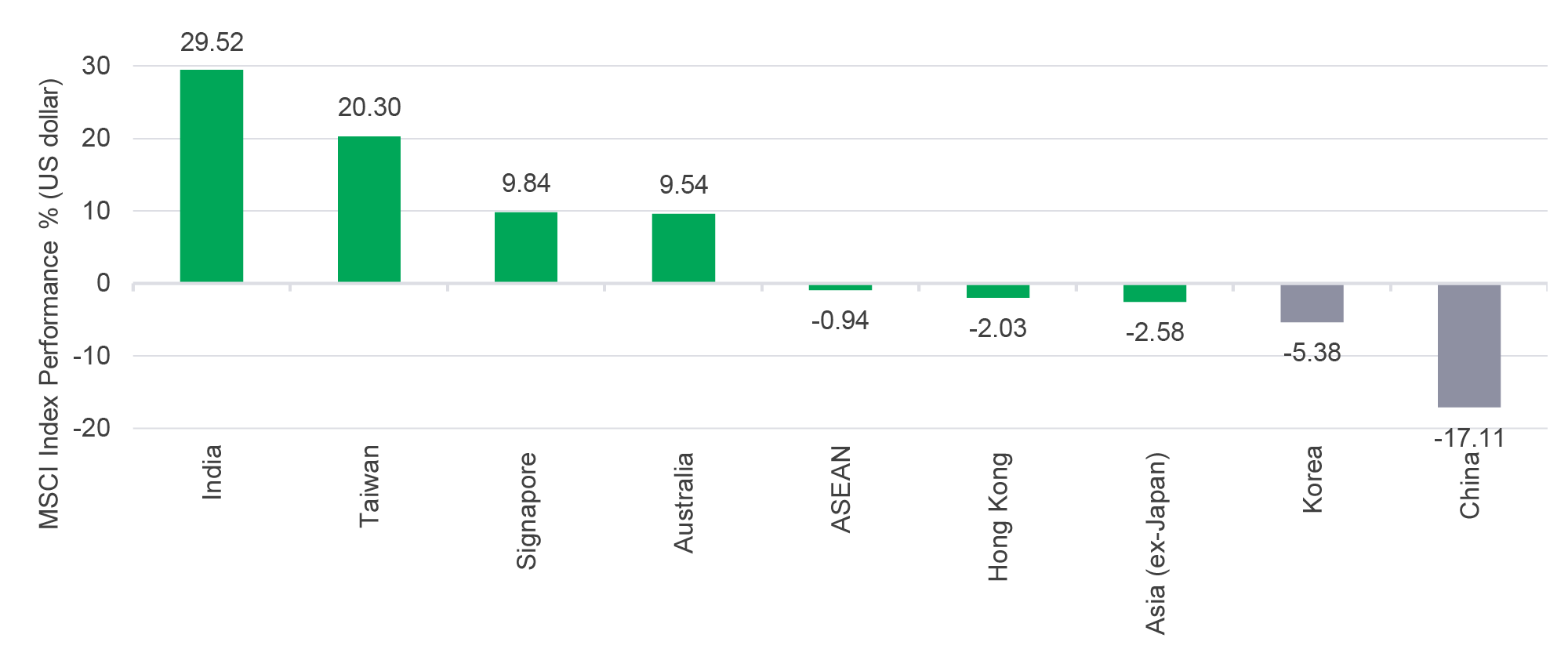
Looking at regional performance year-to-date (24 September 2021), this dynamic has experienced some changes (see Chart 1). Some North Asian markets, such as Taiwan, have continued to perform, while others have fallen along with the worst-performing market, China. India has emerged as the best performing regional market, rebounding after experiencing a second wave of COVID-19 earlier in the year. Meanwhile, ASEAN markets have posted marginally negative performance.
Chart 1: Asian equity market performance, 2021 (YTD)2
After a sharp recovery from the pandemic-driven collapse in economic activity so far in 2021, we expect growth, both globally and across Asia-Pacific, to moderate throughout the rest of 2021. The resurgence of COVID-19 cases, particularly in India, has deferred the highly anticipated economic recovery to the latter part of the year. Even then, the hope of any significant recovery throughout the remainder of the year depends greatly on inoculation rates and each country’s ability to contain the spread of new variants.
On the policy front, the US Federal Reserve (the Fed) adopted a more hawkish tone at its June policy meeting3 and might begin the long process of tapering its monthly asset-purchase programme. This is likely to be one of the most closely watched events moving forward. Other major central banks have also indicated shifts towards a tightening bias4.
In our view, most market participants are not yet ready for tighter monetary policy globally. This is evidenced by companies with negative free cash flow trading at the highest price-to-book (P/B) values, relative to the market, in the past 20 years. The market may be pricing in excessive optimism on these companies, with growth fuelled by external capital rather than organically generated cash flows. However, this may be challenged into a sell-off as bond yields rise.
Inflation may also challenge some companies. Rising raw material prices, freight costs, and the reduced supply of electronic components and semiconductor chips in the first half of 2021 is expected to place pressure on the corporate profits of certain downstream industries. However, we think the impact of cost-push inflation will ease when supply chains across different regions resume to more normal levels.
In China, regulatory and policy risks have recently escalated. While the extensive rollout of new rules and regulations creates short-term pain and may impede the near-term growth of some listed companies, we believe the long-term benefits of stable and orderly development in the affected sectors far outweigh the short-term risks to earnings.
Looking ahead, China’s economic agenda will centre around the development of advanced technology, the real economy, industrialisation and decarbonisation. These are areas where we anticipate policy tailwinds.
For example, we are positive on China’s renewable energy sector – especially companies in the power- grid network and solar-energy supply chain – where we see strong structural growth potential, driven by the government’s goal to reach carbon neutrality by 2060.
The readiness of 5G infrastructure is expected to unleash the potential of segments such as industrial automation, autonomous driving, smart cities, and artificial intelligence. Such development is expected to drive demand for cybersecurity software and services. This area remains underappreciated, in our view.
We also see opportunities in regions outside of China, i.e., Europe, the US, and other emerging markets. This includes companies exposed to the recovery in consumption and investments.
While investors may be concerned about short-term weakness in the tech cycle, we believe the long-term growth outlook for the sector in Taiwan and Korea remains promising. We expect another round of tech-product upgrades to occur in 2022, as tech bellwethers introduce new chips and software that must be supported by new product specifications. Furthermore, the deployment of 5G-related applications remains at a nascent stage of growth, and we believe that momentum will gather pace in 2022.
India suffered a setback after COVID-19 cases spiked during the second wave. But as this appears to be easing and state governments have indicated they will take a more measured approach when easing restrictions, suggesting that a more gradual economic recovery lies ahead. We expect a downward revision in the full-year 2022 earnings estimate before seeing improvements in 2023. Given rising material and commodity prices across the globe, we think that Indian-branded consumer-goods companies face margin pressure.
That said, we see favourable risk-reward characteristics in the following sectors:
Beyond the hyperbole: three macro takeaways from the 2024 US elections
What investors and policy watchers should take away from the 2024 election results depends, in part, on time horizon.
How might the US election and China’s stimulus package impact Asian fixed income?
Asia Fixed Income Team analyses how the US election and other recent major events could impact the region’s fixed income markets.
Assessing China’s latest stimulus measures
Greater China Equities Team analyses the latest round of strategic stimulus and explains why it warrants more than short-term tactical attention. The team also highlights a case study of Chinese companies that are ‘going-global’ to showcase this interesting juncture in the country’s corporate development.
Beyond the hyperbole: three macro takeaways from the 2024 US elections
What investors and policy watchers should take away from the 2024 election results depends, in part, on time horizon.
How might the US election and China’s stimulus package impact Asian fixed income?
Asia Fixed Income Team analyses how the US election and other recent major events could impact the region’s fixed income markets.
Assessing China’s latest stimulus measures
Greater China Equities Team analyses the latest round of strategic stimulus and explains why it warrants more than short-term tactical attention. The team also highlights a case study of Chinese companies that are ‘going-global’ to showcase this interesting juncture in the country’s corporate development.
The recovery in most Southeast Asian countries now looks more subdued following the resurgence of COVID-19 cases. The spread of the more infectious Delta strain amid a relatively slower vaccination rollout has taken its toll on the region’s economy. We now expect a downward revision to growth outlooks for this year. That said, we believe that companies in the following sectors will outperform:
The divergence of Asian equities’ performance thus far in 2021 is poised to continue. North Asian economies and Singapore with higher vaccination rates and better containment measures should have a longer runway for growth. In contrast, the recovery for many ASEAN markets has been delayed and may not occur until the end of 2021 or early 2022. This divergence offers a unique opportunity for active managers to choose quality companies throughout the region.
1 MSCI Asia-Pacific fell 2.58% through 24 September 2021) but there was significant divergence between the best-performing market (India) and worst-performing one (China).
2 Bloomberg, as of 24 September 2021.
3 Transcript of Chair Powell's Press Conference -- June 16, 2021 (federalreserve.gov).
4 People’s Bank of China, European Central Bank, Bank of England, and Reserve Bank of Australia.
5 Multi-national companies based in China to look for another supply chain centre in Asia to diversify supply chains.